Local SEO Basics: How to Rank Higher in Your Area
Introduction
If you have a business that serves a local community, Local SEO is essential for attracting customers nearby. Local SEO helps your business appear in search results when people in your area search for products or services like yours. In this guide, we’ll cover the basics of Local SEO and show you how to optimize your website to rank higher in local searches.
What is Local SEO?
Local SEO is the practice of optimizing your online presence so your business appears in local search results. For example, if someone searches for “coffee shop near me” or “best dentist in [city name],” local SEO helps your business appear in those results.
Why It Matters: Local SEO helps people find businesses close to them, especially when they’re ready to make a purchase. It’s particularly useful for brick-and-mortar stores, restaurants, or any business with a physical location.
Key Elements of Local SEO
- Google My Business (GMB)
- Google My Business is a free tool that allows you to create a profile for your business on Google. This profile appears in local search results and on Google Maps.
- Best Practice: Complete your GMB profile with accurate details like your address, phone number, website, hours, and categories. Add high-quality photos and encourage customers to leave reviews.
- NAP Consistency (Name, Address, Phone Number)
- Ensuring your business name, address, and phone number (NAP) are consistent across all online platforms (GMB, social media, directories, etc.) is critical. Inconsistent information can confuse both search engines and customers.
- Best Practice: Check that your NAP information is identical on all listings and matches what’s on your website.
- Local Keywords
- Using keywords that reflect your location and service area helps attract local customers. For example, instead of “plumbing services,” use “plumbing services in [city name].”
- Best Practice: Include location-based keywords in your page titles, headings, meta descriptions, and content.
- Online Reviews
- Customer reviews on platforms like Google, Yelp, and Facebook can boost your credibility and improve your local rankings. Positive reviews are a trust signal for search engines and potential customers.
- Best Practice: Encourage satisfied customers to leave reviews, and respond to all reviews—both positive and negative—to show you value customer feedback.
- Localized Content
- Creating content related to local events, news, or community interests can help your site rank better for local searches. For instance, a restaurant might blog about local food festivals or events happening nearby.
- Best Practice: Write blog posts, create videos, or offer guides related to your local area to increase engagement and relevance.
Steps to Improve Your Local SEO
1. Claim and Optimize Your Google My Business Listing
- Why It Matters: A fully optimized GMB listing improves your chances of appearing in local search results and the “local pack” (the box showing the top three businesses in a local search).
- How to Do It:
- Log in to Google My Business and claim or create your listing.
- Fill in all relevant details, choose accurate business categories, and upload high-quality photos.
- Keep your hours updated, especially during holidays.
2. Ensure NAP Consistency Across All Platforms
- Why It Matters: Inconsistent information can hurt your local SEO and frustrate potential customers who rely on accurate information to find you.
- How to Do It:
- Audit your business listings on Google, Yelp, Facebook, and other directories to ensure your NAP details are the same everywhere.
- Use a tool like Moz Local or Yext to check your listings and correct any inconsistencies.
3. Use Local Keywords Strategically
- Why It Matters: Local keywords help search engines understand where your business operates and increase your chances of appearing in relevant local searches.
- How to Do It:
- Research local keywords with tools like Google Keyword Planner or Ubersuggest.
- Use these keywords in your website’s title tags, meta descriptions, headers, and throughout your content.
- Create separate pages if you serve multiple locations or nearby cities.
4. Build Local Citations
- What Are They: Local citations are online mentions of your business’s name, address, and phone number on directories, websites, and social media.
- How to Do It:
- List your business on relevant local directories like Yelp, Yellow Pages, and industry-specific sites.
- Ensure your NAP information is accurate on each site.
5. Encourage and Respond to Customer Reviews
- Why It Matters: Reviews not only improve your credibility but also impact your local search rankings. Google considers reviews as a sign of authority and trust.
- How to Do It:
- Ask satisfied customers to leave reviews on Google or Yelp.
- Make it easy for customers by providing a direct link to your Google review page.
- Respond to all reviews, showing appreciation for positive feedback and addressing any issues raised in negative reviews.
6. Optimize for Mobile
- Why It Matters: A large portion of local searches happen on mobile devices. Having a mobile-friendly website is essential for a good user experience and local SEO.
- How to Do It:
- Ensure your site loads quickly and is easy to navigate on mobile.
- Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to check your site’s performance on mobile.
7. Create Locally Relevant Content
- Why It Matters: Content tailored to your local audience can help you stand out in local search results and show your involvement in the community.
- How to Do It:
- Write blog posts about local events, community projects, or tips related to your industry.
- Partner with local influencers or businesses to create content that appeals to your target audience.
- Consider creating a “local resources” page on your site, linking to helpful information related to your area or industry.
Common Local SEO Mistakes to Avoid
- Ignoring Google My Business: Not claiming or optimizing your GMB listing can prevent you from appearing in local search results.
- Inconsistent NAP Information: Inconsistent details across platforms can hurt your local rankings and confuse potential customers.
- Lack of Customer Reviews: Failing to encourage or manage reviews can make your business appear less credible.
- Neglecting Mobile Optimization: A website that’s not mobile-friendly can drive potential customers away, especially on local searches.
Conclusion
Local SEO is a powerful tool for businesses looking to attract customers in their area. By optimizing your Google My Business listing, ensuring NAP consistency, using local keywords, and encouraging customer reviews, you can boost your visibility in local searches and drive more customers to your business. Start by implementing these basics, and over time, you’ll see the benefits of a strong local SEO strategy in the form of increased foot traffic, phone calls, and online engagement. With a little effort and consistency, you can make your business the go-to choice in your community!
SEO vs. SEM: What’s the Difference?
Introduction
If you’re new to digital marketing, terms like SEO and SEM might seem confusing. While they’re often used interchangeably, SEO (Search Engine Optimization) and SEM (Search Engine Marketing) are two different strategies that can help you grow your online presence. Understanding the difference between them can help you decide which approach—or combination—is best for your goals. In this guide, we’ll break down the basics of SEO and SEM, explain their unique benefits, and help you choose the right strategy for your website.
What is SEO?
SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the process of optimizing your website to rank higher in organic (non-paid) search engine results. It involves improving various aspects of your site—such as content, structure, and technical elements—so that search engines like Google can easily understand and rank it.
Key Components of SEO:
- Keyword Research: Finding relevant keywords that people search for and incorporating them naturally into your content.
- On-Page SEO: Optimizing individual pages, including meta tags, headers, and images, to improve relevance.
- Off-Page SEO: Building backlinks from other websites to increase your site’s authority.
- Technical SEO: Ensuring your site loads quickly, is mobile-friendly, and has a clear structure.
Goal of SEO: The primary goal of SEO is to increase organic traffic by ranking higher in search engine results pages (SERPs) without paying for ads.
What is SEM?
SEM, or Search Engine Marketing, is a broader strategy that includes both SEO and paid advertising, such as PPC (Pay-Per-Click) campaigns. SEM’s goal is to increase visibility in search engine results through both organic and paid methods, but it’s often used to refer specifically to paid search advertising.
Key Components of SEM:
- PPC (Pay-Per-Click) Advertising: Running ads that appear in search results and paying each time someone clicks on them.
- Keyword Bidding: Selecting keywords and bidding on them so your ads appear when users search for those terms.
- Ad Copy and Landing Pages: Creating compelling ads and optimized landing pages to increase conversions.
- Analytics and Tracking: Using tools like Google Ads to monitor the performance of your campaigns and optimize them for better results.
Goal of SEM: The primary goal of SEM is to drive targeted traffic to your website quickly through paid search ads, which allows you to appear at the top of search results even before building organic ranking.
SEO vs. SEM: Key Differences
| Aspect | SEO | SEM |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free (but requires time and effort) | Paid, with costs depending on bids and competition |
| Time to Results | Long-term strategy; results may take months | Short-term; immediate visibility when ads are running |
| Sustainability | Lasting impact; continues to drive traffic over time | Stops driving traffic once ads are turned off |
| Placement | Appears in organic search results | Appears in paid ad section at the top of search results |
| Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Often higher because users trust organic results | Lower for paid ads, as some users may skip ads |
| Goal | Build organic traffic over time | Drive traffic immediately, ideal for promotions or launches |
Pros and Cons of SEO
Pros:
- Cost-Effective: SEO is free in terms of direct costs, though it does require time and expertise.
- Long-Term Results: SEO can bring in consistent traffic over time, even without constant updates.
- Higher Credibility: Organic search results are often perceived as more trustworthy by users.
Cons:
- Takes Time to See Results: SEO is a long-term strategy and may take months to show noticeable results.
- Requires Consistent Effort: SEO involves ongoing optimization, content updates, and backlink building.
- Competitive: It can be challenging to rank for highly competitive keywords.
Pros and Cons of SEM
Pros:
- Immediate Results: SEM ads can bring instant visibility and traffic to your site.
- Control Over Targeting: SEM allows you to target specific demographics, locations, and keywords.
- Measurable Results: With SEM, you can track every click and conversion to see the ROI.
Cons:
- Costs Add Up: Unlike SEO, SEM requires a budget, and popular keywords can be expensive.
- Temporary Impact: When you stop paying for ads, the traffic stops immediately.
- Lower Trust: Some users skip ads, preferring organic results.
When to Use SEO vs. SEM
When to Focus on SEO:
- You Have a Long-Term Strategy: If you’re building a brand or blog, SEO is essential for long-term visibility and credibility.
- Budget is Limited: SEO requires effort but doesn’t have a direct cost, making it suitable if you’re starting out on a budget.
- You Want to Build Trust: Organic results are often trusted more than paid ads, making SEO great for establishing authority.
When to Focus on SEM:
- You Need Immediate Traffic: If you’re launching a product, running a limited-time promotion, or need quick traffic, SEM can help drive results fast.
- You Have a Marketing Budget: SEM is ideal if you can afford to spend on ads and want quick returns.
- You’re Testing Keywords: SEM allows you to test different keywords and see which ones perform best before investing in SEO for them.
Using SEO and SEM Together: Many businesses use both SEO and SEM to achieve their goals. For example, you might start with SEM to drive initial traffic while you work on your SEO. Over time, as your organic rankings improve, you can reduce SEM spending and rely more on SEO.
How to Get Started with SEO and SEM
Getting Started with SEO:
- Perform Keyword Research: Identify relevant keywords that people are searching for in your industry.
- Optimize Your Content: Create high-quality, informative content that answers user questions.
- Build Backlinks: Reach out to other sites to link back to your content, increasing your authority.
- Improve Technical SEO: Ensure your site loads quickly, is mobile-friendly, and is easy to navigate.
Getting Started with SEM:
- Set Up a Google Ads Account: Create an account to start running PPC ads.
- Choose Your Keywords: Select targeted keywords based on your audience and goals.
- Create Compelling Ads: Write engaging ad copy and design relevant landing pages.
- Track and Optimize: Use Google Ads and analytics to monitor performance and adjust bids, keywords, or targeting.
Conclusion
Both SEO and SEM are effective ways to drive traffic and grow your online presence, but they serve different purposes. SEO is a long-term, cost-effective strategy for building organic traffic and credibility, while SEM is a fast, targeted approach that requires a budget. By understanding the difference between SEO and SEM, you can choose the strategy that aligns best with your goals—or use both to maximize your reach. Remember, SEO and SEM work well together, so you don’t have to choose just one. With the right balance, you can build a strong foundation for your website’s success.
Understanding Meta Tags: What They Are and How to Use Them
Introduction
Meta tags are one of the simplest yet most effective SEO tools you can use to improve your website’s visibility. While they may seem technical, meta tags are actually easy to understand and implement. They help search engines and users understand what your content is about, increasing your chances of ranking higher. In this guide, we’ll explain what meta tags are, why they matter, and how to use them effectively.
What Are Meta Tags?
Meta tags are snippets of text that describe a page’s content, but they don’t appear on the page itself. Instead, they’re included in the HTML code of your webpage. Meta tags provide information to search engines and visitors about your page’s content, helping to determine if it’s relevant to their search queries.
Example: When you search for something on Google, the title and description you see on the results page come from the page’s meta tags.
Why Are Meta Tags Important?
- Improve Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Meta tags, especially the title and description, are the first things people see in search results. A well-crafted title and description can make your page more attractive to users, increasing clicks.
- Help Search Engines Understand Your Content
- Meta tags give search engines information about what your page covers, making it easier for them to match your content with relevant search queries.
- Control How Your Page Appears in Search Results
- Meta tags allow you to customize the text that appears in search results, giving you a chance to make a good first impression.
- Boost SEO Rankings
- Although meta tags alone won’t skyrocket your rankings, they can enhance your SEO efforts by increasing CTR and improving user experience.
Types of Meta Tags You Should Know
1. Title Tag
- What It Is: The title tag is the main title of your page and appears as the clickable link in search engine results.
- Best Practices:
- Keep it under 60 characters to prevent it from getting cut off in search results.
- Include your main keyword near the beginning.
- Make it clear, concise, and compelling to encourage clicks.
- Example: “10 Delicious Smoothie Recipes for a Healthy Breakfast”
2. Meta Description Tag
- What It Is: The meta description is a short summary of your page’s content. It appears below the title in search results and helps users understand what your page is about.
- Best Practices:
- Keep it between 150-160 characters.
- Include your main keyword naturally.
- Write a compelling description that makes people want to click.
- Example: “Explore 10 easy and delicious smoothie recipes that are perfect for a healthy start to your day.”
3. Meta Keywords Tag
- What It Is: The meta keywords tag used to allow site owners to list specific keywords for search engines. However, Google no longer uses meta keywords for ranking, so it’s generally not necessary today.
- Best Practice: Skip this tag unless you’re optimizing for a search engine that still recognizes it.
4. Robots Meta Tag
- What It Is: The robots meta tag tells search engines what they should or shouldn’t do with a page, such as whether to index it or follow the links on it.
- Best Practices:
- Use
index, followif you want search engines to index your page and follow its links. - Use
noindexif you don’t want the page to appear in search results, like for a thank-you page.
- Use
- Example:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex, follow">
5. Viewport Meta Tag
- What It Is: The viewport tag controls how your page looks on mobile devices, ensuring it scales properly for different screen sizes.
- Best Practices:
- Use it on all your pages, especially if they’re designed to be mobile-friendly.
- Set it to
width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0.
- Example:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
6. Open Graph Meta Tags
- What They Are: Open Graph tags are used to control how your content appears when shared on social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter.
- Best Practices:
- Use
og:title,og:description, andog:imageto customize the title, description, and image shown when your page is shared.
- Use
- Example:
<meta property="og:title" content="10 Delicious Smoothie Recipes"> <meta property="og:description" content="Check out these easy smoothie recipes to start your day right!"> <meta property="og:image" content="https://example.com/smoothie.jpg">
How to Use Meta Tags for Better SEO
1. Optimize Your Title Tag and Meta Description
- Your title and meta description are the first impressions users get of your content. Make them count by including your keyword naturally, keeping them concise, and writing in a way that appeals to your audience’s needs or curiosity.
2. Use Unique Meta Tags for Each Page
- Each page on your site should have a unique title and description to prevent confusion and ensure that search engines know the specific purpose of each page.
3. Avoid Keyword Stuffing
- While it’s important to include your primary keyword, avoid overusing it in your meta tags. Keyword stuffing can make your page look spammy and may hurt your SEO.
4. Consider User Intent
- Think about what users want when they search for your keyword and reflect this intent in your title and meta description. For example, if users are looking for information, use words like “guide” or “how-to.”
5. Use Action Words to Improve CTR
- Action words like “discover,” “learn,” or “find out” can make your meta description more engaging and encourage people to click through to your site.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Meta Tags
- Leaving Meta Tags Blank: Missing meta tags can lead to lower CTR and missed SEO opportunities.
- Duplicating Meta Tags Across Pages: Using the same title or description across multiple pages can confuse search engines and hurt your rankings.
- Ignoring User Experience: Meta tags should be written for humans, not just search engines. Make sure they provide value and clarity to readers.
- Using Outdated Meta Keywords: Meta keywords are no longer relevant for SEO, so focusing on them is a waste of time.
Conclusion
Meta tags are a powerful tool that can help your content stand out in search results. By optimizing your title tags, meta descriptions, and other key meta tags, you can boost your SEO, improve click-through rates, and attract more relevant traffic. Start by reviewing your existing meta tags, making improvements where needed, and keep these best practices in mind as you create new content. With well-optimized meta tags, you’ll be well on your way to improving your site’s visibility and attracting more visitors.
Link Building 101: What It Is and How to Start
Introduction
If you’re new to SEO, you’ve probably heard about “link building” but might not be sure what it means or why it matters. Link building is a critical part of SEO that can help your website rank higher in search results by gaining trust and authority from other sites. In this guide, we’ll break down what link building is, why it’s important, and how you can start building high-quality links for your website.
What is Link Building?
Link building is the process of getting other websites to link to your website. These links, often called “backlinks,” are like votes of confidence from one site to another. When a reputable website links to your content, it signals to search engines like Google that your site is trustworthy and valuable.
Example: Imagine you have a website about home fitness. If a popular fitness blog links to your article on “at-home workouts,” search engines see this link as a positive endorsement, boosting your content’s credibility.
Why is Link Building Important?
- Improves SEO Rankings
- Backlinks are one of Google’s top ranking factors. Websites with more high-quality backlinks generally rank higher in search results.
- Drives Referral Traffic
- Links from other websites can bring new visitors to your site, increasing traffic and potential customer leads.
- Increases Brand Authority
- When reputable sites link to your content, it boosts your brand’s credibility and authority in your industry.
- Helps You Stay Competitive
- Many of your competitors are building links, so investing in link building helps ensure you don’t fall behind in search rankings.
Types of Links in Link Building
Not all links are created equal. Here are the main types of links you should understand:
- Natural Links
- These are links you get organically, without asking for them. They come from other sites that find your content valuable and link to it naturally.
- Manually Built Links
- These links are acquired through deliberate efforts, such as reaching out to bloggers, influencers, or industry sites and asking them to link to your content.
- Self-Created Links
- These are links you place yourself on other sites, like in forums, blog comments, or directories. Be careful with this type, as excessive use can be seen as spammy.
How to Start Link Building: Step-by-Step Guide
1. Create High-Quality, Link-Worthy Content
- The foundation of any link building strategy is creating content that people want to link to. High-quality content that’s informative, unique, or entertaining is more likely to attract backlinks.
- Examples of Link-Worthy Content:
- Comprehensive guides or tutorials
- Data-driven articles or case studies
- Infographics or visual content
- Listicles and “how-to” articles
- Tip: Think about what would be useful or interesting to your audience and focus on providing value.
2. Research and Target Relevant Websites
- Identify websites, blogs, and online publications in your industry that might be interested in linking to your content. Start by looking at sites that link to similar content to yours.
- How to Find Relevant Sites:
- Use tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz to see who links to your competitors.
- Look for industry blogs, news sites, or influencers that cover topics related to your content.
- Tip: Create a list of target websites, and note any contact information or submission guidelines they may have.
3. Reach Out with a Personalized Email
- Once you’ve identified relevant sites, reach out to them with a personalized email explaining why your content might interest their readers. Focus on how your content can add value to their audience.
- How to Write an Outreach Email:
- Keep it short and to the point.
- Mention something specific you like about their website or content.
- Explain why your content would be useful or relevant for their readers.
- Example:
Hi [Name], I came across your article on [topic] and really enjoyed your insights on [specific point]. I recently wrote a detailed guide on [related topic] that I think your readers would find helpful. Here’s the link if you’d like to check it out: [URL]. Thanks for considering it, and keep up the great work! Best, [Your Name]
4. Write Guest Posts
- Guest posting is when you write an article for another website and include a link back to your own site. It’s a great way to get backlinks and reach a new audience.
- How to Find Guest Posting Opportunities:
- Search for sites in your industry that accept guest posts.
- Use search terms like “write for us,” “guest post,” or “contribute” along with your industry keyword.
- Tip: Focus on high-quality websites with strong reputations, as these links will carry more SEO value.
5. Use Broken Link Building
- Broken link building involves finding broken links on other websites, reaching out to the site owner, and suggesting they replace the broken link with a link to your relevant content.
- How to Do It:
- Use tools like Ahrefs or Check My Links (a browser extension) to find broken links on websites in your niche.
- Reach out to the website owner, let them know about the broken link, and suggest your content as a replacement.
- Tip: Approach this as a helpful gesture, offering your content as a way to fix a problem.
6. Leverage Social Media to Boost Visibility
- Sharing your content on social media platforms can increase its visibility, leading to more people seeing and potentially linking to it.
- How to Use Social Media for Link Building:
- Share your articles, infographics, or videos on platforms where your audience is active.
- Engage with followers and influencers by commenting, liking, and sharing their content.
- Tip: Building relationships on social media can lead to natural link opportunities as people share and link to your content.
7. Get Listed in Directories and Local Listings
- Adding your site to reputable directories and local listings can provide relevant backlinks and increase your visibility, especially if you have a local business.
- Best Practices:
- Use high-quality directories like Yelp, Google My Business, and industry-specific directories.
- Avoid low-quality directories or ones that charge for listings, as these may be seen as spammy.
- Tip: Consistency in your business name, address, and phone number across all directories is important for local SEO.
Common Link Building Mistakes to Avoid
- Focusing on Quantity Over Quality: A few high-quality links are far more valuable than many low-quality ones.
- Using Spammy Tactics: Avoid placing links in irrelevant places, such as random blog comments or low-quality forums, as this can hurt your SEO.
- Ignoring Link Relevance: Links from unrelated sites don’t help as much as links from industry-relevant sources.
- Buying Links: Google frowns upon paid links, and they can lead to penalties if detected. Focus on earning links naturally instead.
Conclusion
Link building is a powerful SEO strategy that can significantly improve your website’s visibility and authority. By creating high-quality content, targeting relevant websites, and using outreach and guest posting, you can start building valuable backlinks for your site. Remember, link building takes time and consistency, but the results are worth it. Start small, keep building connections, and watch your site’s rankings improve!
How to Write SEO-Friendly Content That Ranks
Introduction
Writing great content is essential for any website, but to make sure people can find it, you need to make it SEO-friendly. SEO-friendly content is optimized so that it ranks higher in search engines, helping more readers discover your work. In this guide, we’ll break down the steps to create content that’s both useful for readers and optimized for search engines.
What is SEO-Friendly Content?
SEO-friendly content is writing that’s created with search engine optimization (SEO) in mind. This means it’s structured and formatted to help search engines understand it, which increases the chances of ranking higher in search results. The goal is to make your content easy for both users and search engines to read, understand, and appreciate.
Steps to Write SEO-Friendly Content
1. Start with Keyword Research
- Before you begin writing, identify the main keyword for your article. This keyword should reflect what your target audience is searching for, helping your content reach the right people.
- How to Do It: Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ubersuggest, or Ahrefs to find relevant keywords with a good balance of search volume and competition.
- Example: If you’re writing about “healthy smoothie recipes,” related keywords could include “easy smoothie recipes,” “high-protein smoothies,” and “smoothies for weight loss.”
2. Create a Clear Structure with Headings
- Organizing your content with headers (like H1, H2, and H3 tags) makes it easier for both readers and search engines to navigate. Clear headings help search engines understand your main points and improve readability for users.
- How to Do It: Use your primary keyword in the H1 (main heading) and use H2 and H3 tags for subheadings.
- Example:
- H1: “How to Write SEO-Friendly Content That Ranks”
- H2: “What is SEO-Friendly Content?”
- H2: “Steps to Write SEO-Friendly Content”
- H3: “Start with Keyword Research”
3. Write for Humans First, Search Engines Second
- Your content should be easy to read, engaging, and helpful to your readers. Avoid keyword stuffing (using keywords unnaturally or too frequently), as this can hurt your rankings and make the content harder to read.
- Best Practice: Aim for an 8th to 9th-grade reading level, use short sentences, and write in a conversational tone.
- Tip: Use your primary keyword naturally, especially in the first 100 words, but avoid forcing it into every sentence.
4. Use Your Main Keyword Naturally Throughout the Content
- Including your keyword a few times helps search engines understand your content’s topic, but it should feel natural. Place it in important areas like the introduction, subheadings, and conclusion.
- Best Practice: Aim to use your main keyword in the first paragraph, at least one subheading, and in the final paragraph.
- Example: If your main keyword is “healthy smoothie recipes,” you might write an introduction like, “In this guide, we’ll explore healthy smoothie recipes that are quick, delicious, and easy to make.”
5. Include Related Keywords and Synonyms
- Besides your primary keyword, include related terms that add context. These are called “LSI keywords” (Latent Semantic Indexing) and help search engines understand the depth of your content.
- How to Find Them: Look at the “People Also Ask” and “Related Searches” sections in Google or use keyword research tools.
- Example: For “healthy smoothie recipes,” related terms could include “nutritious smoothies,” “easy smoothie recipes,” and “smoothie ingredients for energy.”
6. Optimize Your Meta Description
- The meta description is the short text that appears below your page title in search results. It doesn’t directly affect rankings, but a well-written meta description can improve click-through rates.
- Best Practice: Keep it under 160 characters, include your main keyword, and make it interesting to encourage people to click.
- Example: “Discover easy and healthy smoothie recipes perfect for breakfast, weight loss, and boosting energy!”
7. Add Internal and External Links
- Linking to other pages on your site (internal links) and to reputable sites (external links) can improve your SEO. Internal links help users discover more of your content, while external links show search engines you’re providing credible sources.
- Best Practice: Add 1–2 internal links to other related articles on your website and 1–2 external links to authoritative sources.
- Example: In an article about “healthy smoothie recipes,” you could link to a related article on “benefits of a balanced diet” as an internal link and a reputable nutrition site as an external link.
8. Optimize Images with Alt Text
- Images make your content more engaging, and adding “alt text” (alternative text) helps search engines understand what your images are about. This also improves accessibility for visually impaired users.
- Best Practice: Describe the image accurately and include a keyword if relevant, but avoid keyword stuffing.
- Example: For an image of a smoothie, the alt text could be “Green smoothie made with spinach, banana, and almond milk.”
9. Write a Strong, Keyword-Rich Title
- Your title is the first thing people see in search results, so make it clear, engaging, and include your main keyword. A strong title increases click-through rates and signals to search engines that your content is relevant.
- Best Practice: Keep it under 60 characters and place your main keyword near the beginning.
- Example: “Healthy Smoothie Recipes: Delicious and Nutritious Drinks for Any Time of Day”
10. Keep Your Content Fresh and Up-to-Date
- Search engines prefer content that’s current and relevant. Update your content regularly to ensure it remains useful and accurate for your readers.
- Best Practice: Review and update old articles at least once a year, especially if new information or trends emerge.
- Tip: Add the “Last Updated” date on your posts to show readers and search engines that your content is up-to-date.
Common SEO-Friendly Content Mistakes to Avoid
- Keyword Stuffing: Using keywords too many times can make content hard to read and may lead to penalties.
- Ignoring Meta Descriptions: A missing or poorly written meta description can lower your CTR (click-through rate).
- Not Using Headers: Skipping headers makes content harder to read and less organized.
- Lack of Internal Links: Failing to link to other relevant content on your site can limit user engagement and time spent on your site.
Conclusion
Writing SEO-friendly content doesn’t mean sacrificing quality. By following these steps—such as keyword research, clear structure, and thoughtful use of images—you’ll create content that appeals to both readers and search engines. As you practice, these techniques will become second nature, helping your content rank better and reach more people. Start with one or two of these tips, and soon you’ll be on your way to writing content that ranks!
Top 10 SEO Tools Every Beginner Should Know About
Introduction
Getting started with SEO can feel overwhelming, especially when there’s so much to learn. The good news? There are plenty of SEO tools designed to make your life easier! From researching keywords to tracking your rankings, these tools can help you optimize your website and improve its visibility in search engines. In this guide, we’ll cover the top 10 SEO tools every beginner should know about, with easy-to-understand explanations for each.
1. Google Keyword Planner
- What It Does: Google Keyword Planner helps you find keywords related to your content and shows their search volume and competition level. This makes it easy to find keywords your audience is searching for and understand their popularity.
- Why It’s Great for Beginners: It’s simple to use, and since it’s powered by Google, you get access to data directly from the world’s largest search engine.
- Best Use: Use it for keyword research to find terms that will help your pages rank better in search results.
2. Ubersuggest
- What It Does: Ubersuggest provides keyword suggestions, search volume data, and SEO difficulty scores for keywords. It also gives you content ideas based on your target keywords.
- Why It’s Great for Beginners: The tool is user-friendly and offers valuable insights at an affordable price, making it ideal for beginners.
- Best Use: Use Ubersuggest to find keywords, analyze competitors, and get ideas for content that could rank well.
3. Ahrefs
- What It Does: Ahrefs is an all-in-one SEO tool that covers keyword research, backlink analysis, competitor research, and more. It’s widely known for its strong backlink analysis feature.
- Why It’s Great for Beginners: While Ahrefs is powerful, its interface is intuitive, making it accessible for beginners who want a deeper dive into SEO.
- Best Use: Use Ahrefs to understand your website’s backlink profile, analyze competitor backlinks, and discover content ideas.
4. Google Analytics
- What It Does: Google Analytics tracks website traffic, user behavior, and various metrics related to your content’s performance.
- Why It’s Great for Beginners: Google Analytics is free and offers valuable insights into how users interact with your website, which is essential for SEO success.
- Best Use: Use Google Analytics to track your traffic, see which pages perform well, and monitor user engagement over time.
5. Moz Keyword Explorer
- What It Does: Moz Keyword Explorer provides keyword suggestions, search volume data, and difficulty scores. It’s a comprehensive tool for researching keywords and understanding their potential impact.
- Why It’s Great for Beginners: Moz’s interface is easy to navigate, and it offers tutorials that are helpful for beginners.
- Best Use: Use Moz Keyword Explorer to find low-competition keywords and build your content around search terms that are likely to rank.
6. SEMrush
- What It Does: SEMrush is a popular tool for keyword research, site audits, rank tracking, and competitor analysis. It’s a one-stop shop for SEO data.
- Why It’s Great for Beginners: SEMrush offers a lot of functionality in one tool, so you can experiment with different aspects of SEO in one place.
- Best Use: Use SEMrush to analyze your competitors, monitor your rankings, and find new keywords to target.
7. Answer the Public
- What It Does: Answer the Public generates questions, prepositions, and comparisons related to a keyword, helping you understand what people are asking about your topic.
- Why It’s Great for Beginners: It’s a unique tool that provides valuable insights into what your audience wants to know, which is perfect for creating content that meets their needs.
- Best Use: Use it for content ideas based on questions and topics people are searching for related to your keywords.
8. Yoast SEO (for WordPress)
- What It Does: Yoast SEO is a plugin for WordPress that helps you optimize your content for SEO directly within your website’s backend. It provides a checklist and suggestions to improve readability and keyword use.
- Why It’s Great for Beginners: Yoast makes it easy to optimize on-page SEO elements like meta tags, headings, and keyword density without needing any technical knowledge.
- Best Use: Use Yoast to optimize individual pages and posts, especially if you’re using WordPress to build your website.
9. Screaming Frog SEO Spider
- What It Does: Screaming Frog is a website crawler that analyzes SEO elements on your site, such as broken links, duplicate content, and missing tags.
- Why It’s Great for Beginners: Although it looks complex, Screaming Frog can save you a lot of time by identifying issues that could harm your SEO.
- Best Use: Use Screaming Frog to audit your site and identify any SEO errors that need fixing.
10. Google Search Console
- What It Does: Google Search Console helps you monitor your website’s performance in Google search results. It provides insights into which keywords bring traffic, issues affecting your site’s visibility, and mobile usability.
- Why It’s Great for Beginners: It’s free and provides essential data straight from Google, making it invaluable for tracking your site’s SEO health.
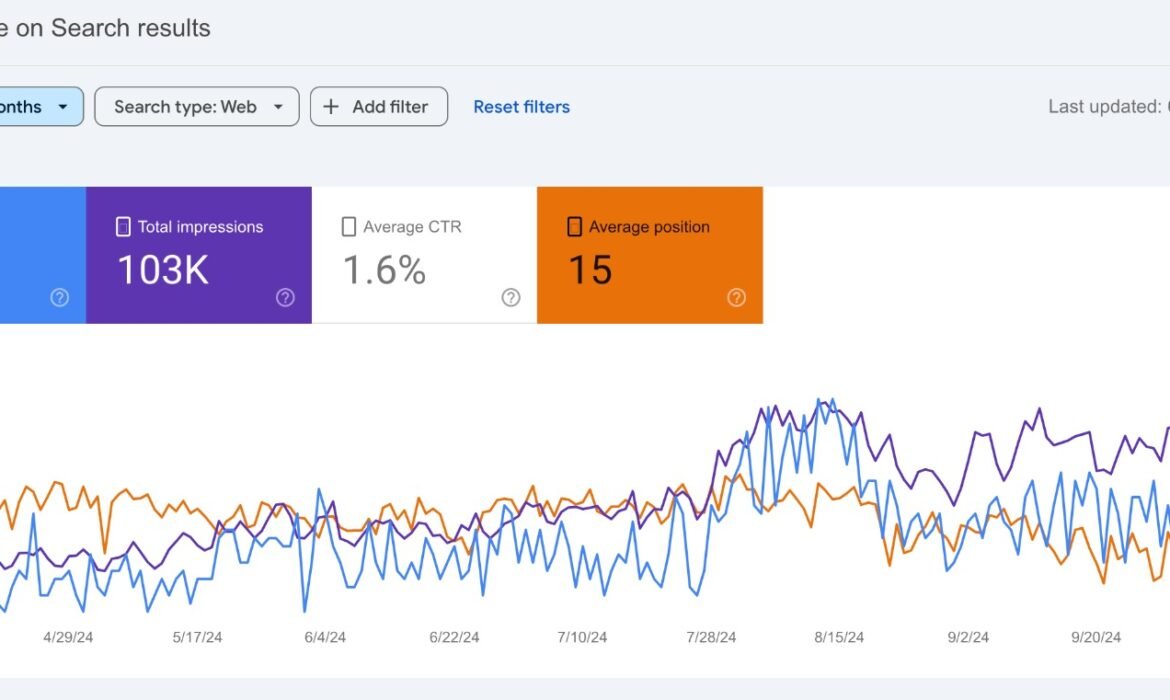
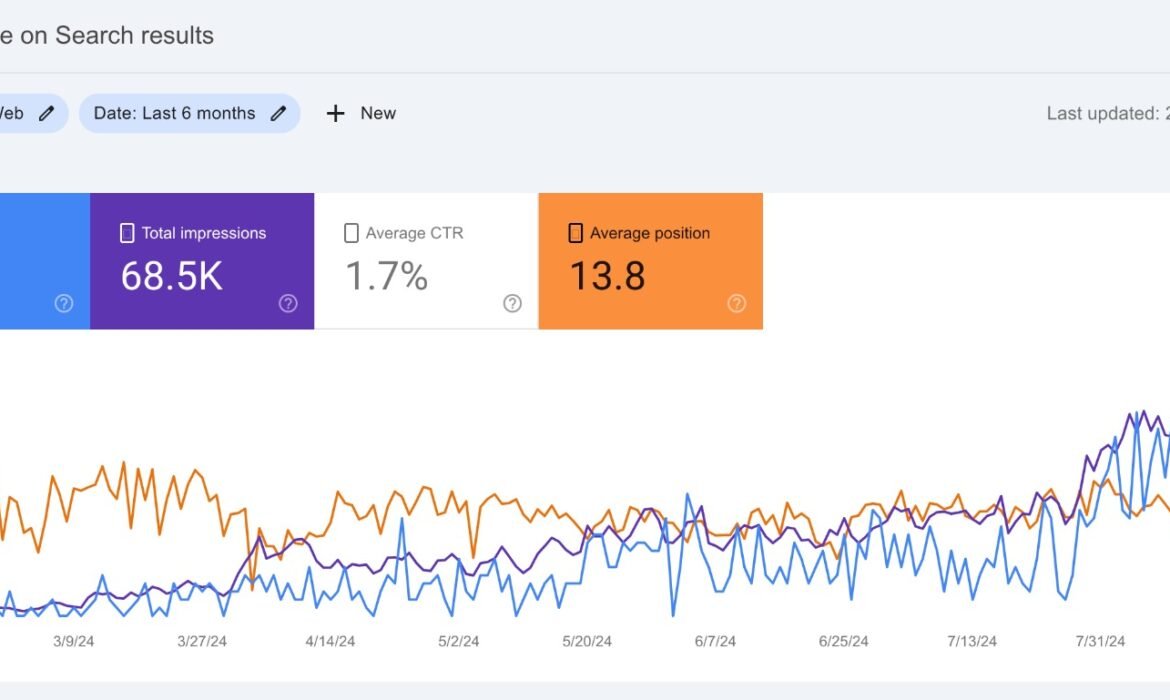
- Best Use: Use Google Search Console to track rankings, analyze clicks and impressions, and identify any issues affecting your search visibility.
How to Choose the Right SEO Tool for You
- Define Your Goals: Do you need help with keyword research, content optimization, or site analysis? Identify what you’re looking to improve.
- Consider Your Budget: Some tools are free or affordable, while others may be more expensive. Choose tools that fit within your budget.
- Test and Experiment: Many SEO tools offer free trials or free versions, so try a few to see which one feels most comfortable for you.
Conclusion
These 10 SEO tools offer a range of capabilities, from keyword research and content optimization to analytics and site audits. As a beginner, start with the basics, such as Google Keyword Planner and Google Analytics, and add tools as your SEO skills grow. Each tool has unique features that can help you improve your site’s performance and visibility. With these tools in your toolkit, you’re well on your way to mastering SEO and growing your website’s traffic. Happy optimizing!
Off-Page SEO Explained: What It Is and How It Helps Your Site Rank
Introduction
When it comes to SEO, you might think that optimizing your website’s content and structure is enough to get high rankings on Google. But there’s another crucial piece of the puzzle: off-page SEO. This involves activities outside your website that boost its authority and relevance. In this guide, we’ll cover what off-page SEO is, why it matters, and the top strategies you can use to improve your website’s ranking.
What is Off-Page SEO?
Off-page SEO refers to actions taken outside of your own website to impact its ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). While on-page SEO focuses on making sure your content is high quality and well-structured, off-page SEO works to increase your site’s authority and trustworthiness in the eyes of search engines.
Example: When other websites link back to your site, it signals to search engines that your content is valuable, trustworthy, and worth ranking higher.
Why Does Off-Page SEO Matter?
- Builds Website Authority
- Search engines use off-page signals to determine the authority and credibility of a website. A site with high authority is more likely to rank higher in search results.
- Boosts Trust and Reputation
- When reputable sites link to your site, it signals to both users and search engines that your content can be trusted. This builds a positive reputation for your brand.
- Increases Visibility and Traffic
- Off-page SEO strategies like link building and social media marketing can help attract more visitors to your site, increasing its visibility online.
- Helps You Outrank Competitors
- Strong off-page SEO can give you an edge over competitors who may have similar on-page SEO but lack a strong backlink profile or social presence.
Top Off-Page SEO Strategies to Boost Your Rankings
1. Link Building
- Link building is the process of getting other websites to link back to your website. These “backlinks” are one of the most important off-page SEO factors, as they show search engines that other sites vouch for your content.
Types of Links to Build:
- Natural Links: Links that websites give you organically, without you asking for them.
- Manual Links: Links you acquire through outreach efforts, like asking bloggers or influencers to link to your content.
- Self-Created Links: Links you create yourself by submitting your site to directories, forums, or comment sections (use sparingly).
Tips for Effective Link Building:
- Create high-quality content that people want to link to.
- Reach out to bloggers and websites in your industry to request relevant links.
- Share your content on social media to increase the chance of natural backlinks.
2. Social Media Marketing
- Social media doesn’t directly impact SEO rankings, but it can help increase your content’s visibility and drive traffic to your site. When people engage with your content on social media, it’s more likely to be shared and even attract backlinks.
Best Practices:
- Share valuable content regularly on platforms where your audience is active.
- Engage with followers by responding to comments and messages.
- Use social media to promote new blog posts, articles, and other content that can attract links.
3. Guest Blogging
- Guest blogging involves writing articles for other websites in your industry, usually in exchange for a backlink to your site. This can help you reach a new audience while building backlinks.
Tips for Guest Blogging:
- Find reputable websites in your industry that accept guest posts.
- Create high-quality, original content that adds value to their readers.
- Make sure the site provides a backlink to your website within your author bio or the article.
4. Influencer Outreach
- Influencer outreach involves building relationships with industry influencers who can help promote your website. Influencers can help generate buzz around your brand and encourage others to visit your site or link to it.
How to Do Influencer Outreach:
- Identify influencers who share content related to your industry.
- Engage with their content (e.g., comment, like, share) to get noticed.
- Reach out with a personalized message offering value, such as a collaboration or mutually beneficial content.
5. Content Marketing and PR
- Content marketing isn’t just about creating content for your site; it also involves distributing that content across other platforms. Through press releases, partnerships, and byline articles, you can increase your visibility and build links.
Tips for Content Marketing and PR:
- Publish helpful guides, infographics, and case studies that other sites may want to link to.
- Use press releases to announce newsworthy developments in your business.
- Submit articles to industry publications or contribute to reputable websites.
6. Forum and Community Engagement
- Participating in forums, Q&A sites, and online communities like Quora and Reddit can help establish your authority and provide opportunities to share your content when it’s relevant.
Best Practices for Forums:
- Only post on forums and communities that allow self-promotion.
- Provide helpful answers and only include a link when it genuinely adds value.
- Avoid spammy behavior—always contribute positively to the conversation.
7. Local Listings and Directories
- If you run a local business, listing your site in directories and on local listing sites like Google My Business, Yelp, and Yellow Pages can boost your visibility in local search results.
Best Practices for Local Listings:
- Ensure your business name, address, and phone number (NAP) are consistent across all listings.
- Encourage customers to leave reviews on your business listings.
- Add relevant keywords and descriptions to your listings to improve searchability.
8. Brand Mentions
- Brand mentions are when other websites mention your brand or website, even without a link. This can still help boost your visibility and build your reputation.
Tip: Set up Google Alerts for your brand name to track mentions across the web. If you notice a site mentioning your brand without linking to it, you can reach out and request a backlink.
Common Off-Page SEO Mistakes to Avoid
- Low-Quality Backlinks: Avoid getting backlinks from spammy or irrelevant websites, as this can harm your SEO rather than help it.
- Over-Linking in Comments: Posting your link in unrelated comment sections or forums can look spammy and may lead to penalties.
- Focusing Only on Quantity: Quality matters more than quantity in link building. Focus on earning a few high-quality links rather than many low-quality ones.
- Ignoring Social Media: Social media may not directly impact rankings, but it can drive traffic and increase the chance of backlinks.
Conclusion
Off-page SEO is all about building authority, credibility, and visibility for your website beyond its content and design. By implementing off-page SEO strategies like link building, social media marketing, and influencer outreach, you can boost your site’s ranking and attract more visitors. Remember, off-page SEO takes time and effort, but it’s worth it for the long-term growth and success of your website. Start with one or two strategies, track your progress, and watch your website’s reputation and rankings grow!
On-Page SEO Made Easy: Simple Steps to Optimize Your Pages
Introduction
Getting your website to rank higher on Google and other search engines doesn’t have to be complicated. On-page SEO is all about optimizing individual pages on your website to improve their visibility in search engines. The good news? With a few simple steps, you can make a big impact! In this guide, we’ll go over the basics of on-page SEO and give you easy-to-follow steps to optimize your pages effectively.
What is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO involves optimizing the content and HTML source code of a page. It’s different from off-page SEO, which focuses on external factors like backlinks. With on-page SEO, you have direct control, allowing you to make your pages more appealing to search engines and users alike.
Example: If you run a fitness blog and have an article about “home workouts for beginners,” on-page SEO will help that page rank higher when someone searches for “beginner home workouts” or “how to work out at home.”
Why is On-Page SEO Important?
- Improves Visibility and Rankings
- On-page SEO helps search engines understand what your page is about, making it more likely to appear in relevant search results.
- Boosts User Experience
- Optimized pages are easier to read and navigate, which keeps visitors on your site longer—another factor that can improve your rankings.
- Increases Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Pages with clear, relevant titles and descriptions attract more clicks from search results, leading to higher traffic.
- Drives Targeted Traffic
- On-page SEO helps attract people who are looking for specific information, making it easier to connect with the right audience.
Simple Steps to Optimize Your Pages
1. Start with Keyword Research
- Before you begin, identify the main keyword for each page. This keyword should reflect what the page is about and match what your target audience is searching for.
Example: For a page about “best running shoes,” make “best running shoes” your main keyword.
2. Optimize Your Title Tag
- The title tag is one of the most important on-page SEO elements. It’s the headline that appears in search results, so make sure it’s both informative and includes your main keyword.
Best Practice: Keep your title tag under 60 characters and place the main keyword at the beginning.
Example: “Best Running Shoes for Every Type of Runner in 2024.”
3. Write a Compelling Meta Description
- The meta description is a short summary of your page’s content. It doesn’t directly impact rankings but can boost your CTR by making people more likely to click on your page in search results.
Best Practice: Keep it between 150-160 characters and include your main keyword. Make it interesting to encourage clicks.
Example: “Discover the best running shoes for every type of runner, from beginners to marathoners. Find the perfect pair for your needs!”
4. Use Headers and Subheaders (H1, H2, H3, etc.)
- Organize your content with headers. The H1 tag should contain the main topic or title of your page, while H2s and H3s break down different sections.
Best Practice: Use only one H1 per page (usually the page title) and include your main keyword here. Use H2s and H3s for subtopics.
Example:
- H1: “Best Running Shoes for Every Type of Runner in 2024”
- H2: “Top Features to Look for in Running Shoes”
- H2: “Best Running Shoes for Beginners”
- H3: “Lightweight and Cushioned Options”
5. Include Keywords Naturally in the Content
- Your main keyword and related keywords should appear naturally in the content. Avoid overusing keywords (called “keyword stuffing”) as this can hurt your rankings.
Best Practice: Aim to use your main keyword once in the first 100 words and then naturally throughout the content. Also, use variations and related terms to keep it natural.
Example: If your main keyword is “best running shoes,” variations could include “top running shoes” or “running shoe reviews.”
6. Optimize Image Alt Text
- Images add value to your content and can also help with SEO. Use descriptive, keyword-rich alt text (alternative text) to explain what each image is about.
Best Practice: Use short, descriptive alt text that includes keywords where relevant.
Example: Alt text for an image of a pair of running shoes could be “Lightweight running shoes for beginners.”
7. Make URLs SEO-Friendly
- URLs should be short, descriptive, and include your main keyword. Avoid long, complicated URLs with random numbers or irrelevant information.
Best Practice: Keep URLs under 60 characters and use hyphens to separate words.
Example: “/best-running-shoes” instead of “/products/12345-best-running-shoes.”
8. Use Internal Links
- Internal links connect pages on your site, making it easier for visitors to find related content and for search engines to understand your site structure.
Best Practice: Link to other relevant pages on your site naturally within the content.
Example: If you mention “strength training” in a blog post about fitness, link it to another post about strength training exercises.
9. Improve Page Load Speed
- Page speed is a key ranking factor. Slow-loading pages can hurt your rankings and drive visitors away.
Best Practice: Compress images, use caching, and consider a content delivery network (CDN) to improve load times.
Tip: You can test your page speed with Google’s PageSpeed Insights and follow their recommendations to improve it.
10. Make Sure Your Site is Mobile-Friendly
- More than half of all searches come from mobile devices, so your site should be easy to read and navigate on a phone.
Best Practice: Use responsive design, which automatically adjusts your page layout based on the device.
Tip: Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test can tell you if your site meets mobile-friendly standards.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in On-Page SEO
- Keyword Stuffing: Avoid overusing keywords, as this can lead to penalties and make your content hard to read.
- Ignoring Meta Descriptions: Skipping the meta description means missing an opportunity to increase clicks from search results.
- Not Updating Content: Outdated content can hurt your rankings. Regularly update your pages to keep them relevant.
- Using Poor-Quality Images: High-quality images are essential. Poor or slow-loading images can hurt your user experience and SEO.
Conclusion
On-page SEO may seem overwhelming at first, but by following these simple steps, you can create optimized, user-friendly pages that are easy for search engines to understand. Remember that on-page SEO is not a one-time task; it’s an ongoing process. As you create new content and update existing pages, keep these practices in mind, and you’ll start seeing results over time. Start small, experiment, and watch your pages climb the search rankings!
The Basics of Keyword Research: How to Find the Right Keywords for Your Website
Introduction
If you’re starting out with SEO, you’ve probably heard the term “keyword research.” But what exactly is it, and why is it so important? Keyword research is the foundation of SEO, helping you understand what people are searching for online so you can create content that answers their questions. In this guide, we’ll walk you through what keyword research is, why it matters, and how to find the best keywords for your website.
What is Keyword Research?
Keyword research is the process of identifying the specific words and phrases people use to search for information on a topic. By discovering the terms your target audience is using, you can better understand their needs and create content that matches their intent. Essentially, it’s about speaking the language of your audience and helping your website appear in the right searches.
Example: If you run a baking blog, some relevant keywords might be “how to bake bread,” “easy cake recipes,” or “best baking tools.” Each of these terms reflects what people might type into a search engine when looking for baking advice.
Why is Keyword Research Important?
- Helps Drive the Right Traffic
- By targeting specific keywords, you’re attracting people who are already interested in what you offer. This means more relevant traffic that’s likely to convert.
- Guides Your Content Strategy
- Keyword research reveals the topics your audience cares about. This helps you create content that’s both valuable to readers and optimized for search engines.
- Boosts SEO Rankings
- Optimizing for the right keywords can improve your chances of ranking higher in search results. The better you rank, the more visibility you’ll have.
- Increases ROI for Your Efforts
- Time spent on keyword research pays off by ensuring that your content reaches people who are most likely to be interested in your website or business.
How to Find the Right Keywords: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Brainstorm Seed Keywords
Start by thinking of general terms related to your website or business. These are called “seed keywords” and will be the foundation of your keyword research. Ask yourself, “If I were a potential visitor, what would I search for?”
Example: If you have a gardening blog, seed keywords could be “gardening tips,” “how to grow vegetables,” or “best plants for beginners.”
2. Use Keyword Research Tools
Many tools are available to help you find relevant keywords. Here are a few popular options:
- Google Keyword Planner: Google’s tool provides keyword suggestions, search volume, and competition level.
- Ubersuggest: This free tool offers keyword ideas, search volume, and SEO difficulty scores.
- Answer the Public: Enter a seed keyword, and this tool will show you common questions people ask around that topic.
These tools generate ideas based on real user searches, helping you discover keywords you may not have thought of.
3. Analyze Search Volume and Competition
Not all keywords are created equal. Some keywords have high search volumes (meaning lots of people search for them), while others have lower volumes. In general:
- High-Volume Keywords: These have more traffic potential but often come with more competition.
- Low-Volume Keywords: These may have less competition but also attract a smaller audience.
Tip: It’s usually best to find a balance. Aim for “medium-volume” keywords that have decent search volume but aren’t too competitive, especially if your website is new.
4. Look for Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases that have lower search volume but higher intent. Because they’re more specific, long-tail keywords tend to have less competition and attract users who are closer to making a decision.
Example: Instead of “gardening tips,” a long-tail keyword might be “gardening tips for small backyards.” This is more specific and likely to attract users looking for exactly that information.
5. Analyze User Intent
User intent is what a searcher aims to achieve with their search. Are they looking to buy something, find information, or compare products? There are typically three types of search intent:
- Informational: Searching for information (“how to grow tomatoes”).
- Navigational: Looking for a specific website or brand (“Facebook login”).
- Transactional: Ready to make a purchase or take action (“buy garden tools online”).
Tip: For informational websites, focus on keywords with informational intent. For e-commerce sites, target transactional keywords that show buying intent.
6. Check Out Your Competitors
Look at what keywords your competitors are targeting. You can use tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or even a simple Google search to see which keywords similar websites are ranking for. This helps you identify gaps in their content that you could fill or find keywords that might be easier to rank for.
7. Organize and Prioritize Your Keywords
Once you have a list of keywords, organize them based on factors like search volume, competition, and relevance. Prioritize keywords that best match your audience’s needs and align with your goals. By creating a structured list, you’ll be able to build your content strategy around these keywords.
Putting Keywords into Action: Tips for Using Keywords on Your Website
- Include Keywords in Your Titles and Headings
- Titles and headings tell both users and search engines what your page is about. Use your main keyword in the title and relevant subtopics in headings.
- Use Keywords Naturally in Content
- Avoid “keyword stuffing,” or overusing keywords. Instead, use them naturally throughout your content, especially in the first paragraph and in places where they fit organically.
- Optimize Meta Descriptions and URLs
- The meta description is the brief text that appears under your page title in search results. Including your main keyword here can help improve click-through rates. Also, make your URLs short and include the keyword when possible.
- Use Images with Alt Text
- Adding images with alt text (descriptions of the image) that include keywords helps search engines understand the content better, as well as improve accessibility for visually impaired users.
- Internal and External Linking
- Use internal links to guide users to related content on your site. External links to reputable sources can also enhance the quality of your content.
Conclusion
Keyword research is an essential part of SEO that helps you reach the right audience with the right content. By understanding how to find and use keywords effectively, you’ll be able to create content that ranks well, attracts more visitors, and keeps them engaged. Start with the basics, experiment with different keywords, and adjust your strategy as you learn more about what your audience is searching for. Happy keyword hunting!
SEO : What is SEO and Why Does It Matter?
Introduction
Have you ever wondered why some websites appear at the top of a Google search while others are buried on page 10? That’s where SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, comes in. If you’re just starting with SEO, don’t worry! In this guide, we’ll break it down step-by-step so you can understand what SEO is, why it matters, and how it can help your website grow.
What is SEO?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. It’s a process that helps your website appear higher in search engine results, like Google or Bing, when people search for terms related to your business. The higher your website ranks, the more likely people are to find it. Think of SEO as the process of making your website more “search engine-friendly,” so search engines will want to show it to people.
Example: If you have a website that sells organic coffee, SEO can help your site appear at the top when someone searches for “buy organic coffee online.”
Why Does SEO Matter?
- Increases Website Traffic
- SEO helps bring people to your website. When your site appears at the top of search results, it gets more clicks, which means more visitors.
- Builds Trust and Credibility
- High-ranking websites are often seen as trustworthy by search engines and users alike. When people see your site on the first page, they’re more likely to trust your brand.
- Improves User Experience
- SEO isn’t just about keywords and search engines; it’s about creating a better experience for your users. This includes faster loading times, mobile-friendly design, and relevant content, which keeps visitors on your site longer.
- Drives Long-Term Results
- Unlike paid ads, which disappear when you stop paying, SEO efforts can last for months or even years. Once your website starts ranking well, you’ll continue to get traffic without constantly paying for ads.
How Does SEO Work?
SEO may seem complex, but it breaks down into a few main parts:
- Keyword Research
- Keywords are the words and phrases people type into search engines. Finding the right keywords for your website helps you target what your potential customers are searching for.
- On-Page SEO
- This focuses on optimizing parts of your website you control, like content, headers, meta descriptions, images, and internal links. Good on-page SEO helps search engines understand what your website is about.
- Off-Page SEO
- This is about building your website’s reputation through external sources, such as other websites linking to yours. When a trusted site links to yours, it’s like a vote of confidence that your website is trustworthy.
- Technical SEO
- Technical SEO covers things like site speed, mobile-friendliness, and secure connections (HTTPS). These aspects make your website more accessible and easy to navigate, which can improve its ranking.
The Benefits of SEO for Your Website
SEO can transform your website and brand in a few key ways:
- More Visitors, More Leads
Higher rankings mean more visitors to your site, which means more chances to convert visitors into customers. - Cost-Effective Marketing
Unlike paid ads, which stop working once you stop paying, SEO keeps bringing visitors over time, making it a more cost-effective marketing strategy. - Competitive Advantage
Many businesses are already using SEO, and getting started can give you an edge over competitors who aren’t optimizing their sites.
Getting Started with SEO
If you’re ready to get started with SEO, here are a few simple steps:
- Identify Your Keywords
Start by researching keywords related to your business. Tools like Google Keyword Planner or Ubersuggest can help you find relevant keywords. - Optimize Your Content
Make sure your content is clear, engaging, and uses your chosen keywords naturally. Avoid keyword stuffing (overusing keywords) because it can hurt your rankings. - Make Your Site User-Friendly
Ensure your website is fast, mobile-friendly, and easy to navigate. User experience is crucial in SEO! - Build Backlinks
Try to get other reputable websites to link to yours. This can be done by reaching out to bloggers, getting listed in directories, or creating shareable content. - Track Your Progress
Use tools like Google Analytics or Google Search Console to see how your site performs. Tracking your progress helps you see what’s working and where you can improve.
Conclusion
SEO might seem overwhelming at first, but it’s one of the most effective ways to get more visitors to your website. By understanding what SEO is and why it matters, you’re already on the path to growing your online presence. Take it step-by-step, focus on creating quality content, and make your website user-friendly. Soon, you’ll start seeing results and enjoying the benefits of SEO for your business!